Blood disorders occur when the cells in the blood do not function as they should, causing certain symptoms and related issues. The most common blood abnormalities are as follows
Anemia
People with anemia have a low number of red blood cells. Mild anemia often causes no symptoms. More severe anemia can cause fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath with exertion.
Thalassemia
This is a genetic form of anemia that affects the body’s ability to produce hemoglobin and red blood cells. These patients may need regular blood transfusions to relieve anemia symptoms.
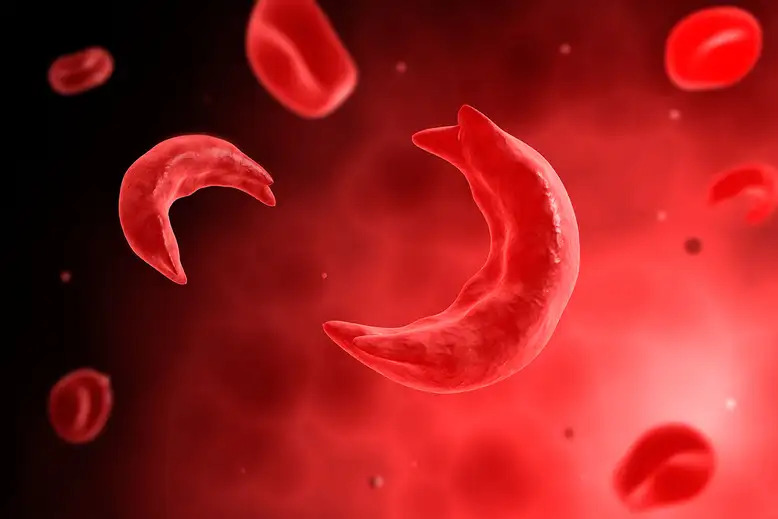
Sickle cell anemia
A genetic condition that causes the red blood cells to be sticky and stiff, which obstructs proper blood flow. Severe pain and organ damage can occur.
Polycythemia vera
The body produces too many red blood cells, from an unknown cause. The excess red blood cells usually create no problems, but may cause blood clots in some people and can turn fatal.
Lymphoma
A form of blood cancer that develops in the lymph system. In lymphoma, a white blood cell becomes malignant, multiplying and spreading abnormally. Treatment with chemotherapy and/or radiation can often extend life with lymphoma, and sometimes cure it.
Leukemia
A form of blood cancer in which a white blood cell becomes malignant and multiplies inside bone marrow. Leukemia may be acute (rapid and severe) or chronic (slowly progressing). Chemotherapy and/or stem cell transplantation (bone marrow transplant) can be used to treat leukemia, and may result in a cure.
Multiple myeloma
A blood cancer in which a white blood cell called a plasma cell becomes malignant. The plasma cells multiply and release damaging substances that eventually cause organ damage. Multiple myeloma has no cure, but stem cell transplant and/or chemotherapy can improve longevity.
Thrombocytopenia
A low number of platelets in the blood; numerous conditions can cause thrombocytopenia, but most are not severe and do not result in abnormal bleeding.
Purpura
A condition causing a persistently low number of platelets in the blood, due to an unknown cause; usually, there are no symptoms, yet abnormal bruising, small red spots on the skin, or abnormal bleeding can result.
Von Willebrand disease
It is an inherited bleeding disorder. People with von Willebrand disease can have heavier-than-normal bleeding after an injury, surgery, menstrual flow and childbirth. In rare cases, this condition can be fatal.
Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a rare, inherited bleeding disorder in which blood cannot clot normally at the site of a wound or injury. The disorder occurs because certain blood clotting factors are missing or do not work properly. Because a clot does not form, extensive bleeding can be caused from a cut or wound. This is called external bleeding. Bleeding inside the body, called internal bleeding, can occur as well, especially in muscles and in joints like the hips and knees.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply